Basic Examples - Java Generation
Note: These examples are valid for the 2.x version of the plugin, and do not necessarily work for the jaxb2-maven-plugin version 1.x
These basic examples show how to generate Java code from JAXB using the jaxb2-maven-plugin, and highlight the use of some of the plugin's common configuration options.
This plugin runs the XJC binding compiler from the JAXB distribution, and integrates XJC's configuration properties into a Maven project. The plugin will delegate all JAXB-related work to its JAXB implementation dependencies. The actual JAXB dependencies used when compiling the plugin will also be collected and listed when the plugin is run in debug mode.
Due to the construction of the Java platform the JAXB API used is the one defined by the platform. This means that the used JAXB API version will be the endorsed one of the JDK, regardless of what is specified in the plugin (or its dependencies). You may override the endorsed API outside of Maven and this plugin, but that is typically viewed as advanced usage. A better option is to align the version of the compiled code with the requirement on the JAXB runtime environment of the generated code.
Note: The plugin currently requires that you run it from within the maven project directory,
i.e. where the pom.xml file resides. If the project is part of a multi-module Maven build,
Maven will take care of this for you.
Standard (implicit) configuration
To find which files should be included within an XJC compilation the jaxb2-maven-plugin uses the following algorithm. Note that the find-and-filter algorithm is applied to find both XSD files and XJB files.
- Find source files. Source files are either given as an explicit path, or found by recursively listing
all files below a source directory given as an explicit path. For example, if
<source>src/main/xsd</source>is the relative path to a directory, all files within it would be found. - Filter source files. A (set of) exclude Filters are applied to each found source file. Any file matching at least one Filter is excluded from the XJC compilation.
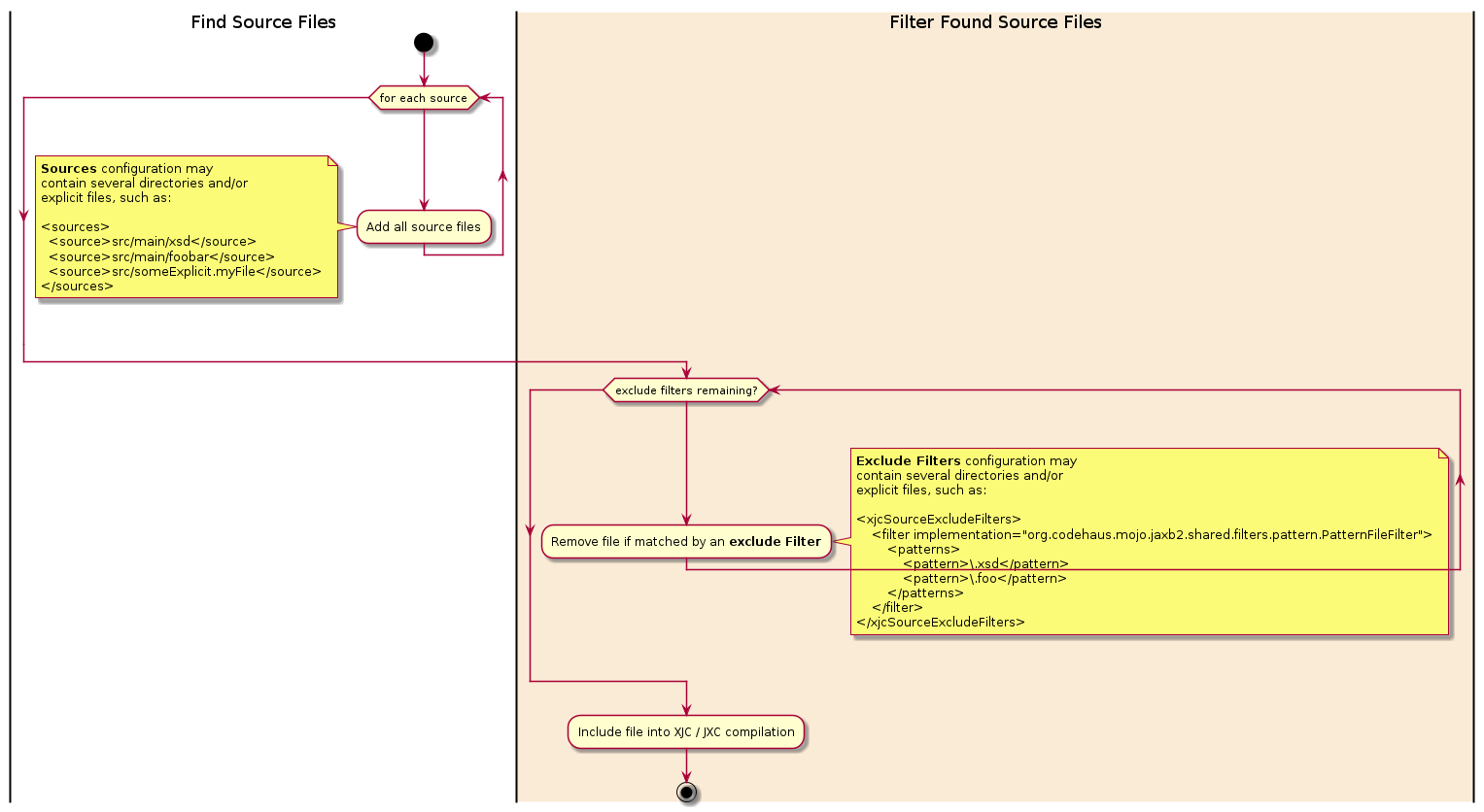
Unless overridden by the configuration, the following settings are used by default:
- The
src/main/xsddirectory (including subdirectories) is expected to contain compile-scope XSD files, as documented within theXjcMojo.STANDARD_SOURCE_DIRECTORYproperty. By default, files matching some Java Regexp patterns are excluded from the XJC compilation. The default exclude patterns are"README.*", "\.xml", "\.txt", "\.java", "\.scala", "\.mdo". - The
src/test/xsddirectory (including subdirectories) is expected to contain test-scope XSD files, as documented within theTestXjcMojo.STANDARD_TEST_SOURCE_DIRECTORYproperty. By default, files matching some Java Regexp patterns are excluded from the XJC compilation. The default exclude patterns are"README.*", "\.xml", "\.txt", "\.java", "\.scala", "\.mdo". - The
src/main/xjbdirectory (including subdirectories) is expected to contain compile-scope XJB files, as documented within theXjcMojo.STANDARD_XJB_DIRECTORYproperty. By default, files matching some Java Regexp patterns are excluded from the XJC compilation. The default exclude patterns are"README.*", "\\.xml", "\\.txt", "\\.xsd". - The
src/test/xjbdirectory (including subdirectories) is expected to contain test-scope XJB files, as documented within theTestXjcMojo.STANDARD_TEST_XJB_DIRECTORYproperty. By default, files matching some Java Regexp patterns are excluded from the XJC compilation. The default exclude patterns are"README.*", "\\.xml", "\\.txt", "\\.xsd".
The standard behavior can be overridden by the following elements:
sources- replacesrc/main/xsdas the directory containing XSD filesxjbSource- replacesrc/main/xjbas the directory containing XJB filesxjcSourceExcludeFilters- replace the default Filters for XSD file exclusionsxjbExcludeFilters- replace the default Filters for the XJB file exclusions
For test-scope XJC compilation, the following configuration elements can be used to override the default behavior:
testSources- replacesrc/test/xsdas the directory containing (test-scope) XSD filestestXjbSources- replacesrc/test/xjbas the directory containing (test-scope) XJB filestestSourceExcludeFilters- replace the default Filters for (test-scope) XSD exclusionstestXjbExcludeFilters- replace the default Filters for (test-scope) XJB exclusions.
These configuration options are illustrated within the examples below. Also, feel free to investigate the integration tests of the plugin itself.
Example 1: Generate Java code within provided package
The plugin will process all XSD files found within the source directories,
and create Java source code in the given package (com.example.myschema) as defined by the packageName
configuration parameter. The required JAXB runtime version of the generated code will be the same as the
plugin's JAXB implementation dependency (see the target parameter).
<project>
...
<dependencies>
<!--
You need the JAXB API to be able to annotate your classes.
However, starting with Java 6 that API is included in the
Java SE platform so there is no need to declare a dependency.
-->
...
</dependencies>
...
<build>
<pluginManagement>
<plugins>
<!--
If we e.g. execute on JDK 1.7, we should compile for Java 7 to get
the same (or higher) JAXB API version as used during the xjc execution.
-->
<plugin>
<groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId>
<artifactId>maven-compiler-plugin</artifactId>
<configuration>
<source>1.7</source>
<target>1.7</target>
</configuration>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</pluginManagement>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.codehaus.mojo</groupId>
<artifactId>jaxb2-maven-plugin</artifactId>
<version>${project.version}</version>
<executions>
<execution>
<id>xjc</id>
<goals>
<goal>xjc</goal>
</goals>
</execution>
</executions>
<configuration>
<!-- The package of your generated sources -->
<packageName>com.example.myschema</packageName>
</configuration>
</plugin>
...
</plugins>
</build>
...
</project>
Example 2: Aligning JDK with JAXB API and JAXB runtime environment
So you want to use JAXB on JDK 8? You would then need to configure the jaxb2-maven-plugin for a Java 8+ project, which implies two separate configuration properties:
- maven-compiler-plugin: Define java version 8 for the compiler, to use the Java 8+ platform as the runtime
environment for the compiled code. Use 1.8 for both the
sourceandtargetproperties. - jaxb-maven-plugin: Use the
targetconfiguration parameter to set the JAXB runtime version to 2.1, which is included in the JDK 1.6 (starting with JDK 1.6u4).
The project can now be built with JDK 8.
<project>
...
<build>
<pluginManagement>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId>
<artifactId>maven-compiler-plugin</artifactId>
<configuration>
<source>1.8</source>
<target>1.8</target>
</configuration>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</pluginManagement>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.codehaus.mojo</groupId>
<artifactId>jaxb2-maven-plugin</artifactId>
<version>${project.version}</version>
<executions>
<execution>
<id>xjc</id>
<goals>
<goal>xjc</goal>
</goals>
</execution>
</executions>
<configuration>
<target>2.1</target>
...
</configuration>
</plugin>
...
</plugins>
</build>
...
</project>
Example 3: Using another type of input source
Normally, you would use XML Schema Definitions as the standard type of JAXB source.
However, other standards can be used as source type provided that the configuration parameter sourceType
is assigned one of the existing values of the
org.codehaus.mojo.jaxb2.javageneration.SourceContentType
enum. In the example below, the source files contain
Document Type Descriptions instead of XML Schema, and
they are placed within the src/main/dtd directory.
Note that the sourceType configuration parameter is case sensitive for matching the enum values.
Refer to the plugin's JavaDoc to see all possible values.
<plugin>
<groupId>org.codehaus.mojo</groupId>
<artifactId>jaxb2-maven-plugin</artifactId>
<version>${project.version}</version>
<executions>
<execution>
<id>xjc</id>
<goals>
<goal>xjc</goal>
</goals>
</execution>
</executions>
<configuration>
<!-- Set the package of the generated code -->
<packageName>com.example.myschema</packageName>
<!-- Indicate that we should use DTD input instead of XSDs -->
<sourceType>dtd</sourceType>
<!-- Define the directory where we should find the DTD files -->
<sources>
<source>src/main/dtd</source>
</sources>
</configuration>
</plugin>
Example 4: Defining sources and XJC exclude filters
By default, the jaxb2-maven-plugin examines the directory src/main/xsd for XSD files
which should be used by JAXB to create Java source code (and src/test/xsd for test XSD sources).
If you would like to place your XSD somewhere else, you need to define source elements
as shown in the configuration below. The paths given are interpreted relative to
the basedir property, which is set to reference the maven project directory.
Files found (using a recursive search) within the sources elements are read and used by the XJC tool
only if they are not matched by any xjcSourceExcludeFilters. Therefore, the configuration below
should include src/main/some/other/xsds/aFile.txt as an XSD source,
but exclude src/main/some/other/xsds/thisIsASource.xsd due to the pattern definition
<pattern>\.xsd</pattern>. (For a full explanation of filters, please refer to the
Filters documentation).
<plugin>
<groupId>org.codehaus.mojo</groupId>
<artifactId>jaxb2-maven-plugin</artifactId>
<version>${project.version}</version>
<executions>
<execution>
<id>xjc</id>
<goals>
<goal>xjc</goal>
</goals>
</execution>
</executions>
<configuration>
<!--
Include the sources from 3 locations:
1) a directory (including recursively finding all files in it)
2) an explicitly named file
3) a non-existent path, which is silently ignored
-->
<sources>
<source>src/main/some/other/xsds</source>
<source>src/main/foo/gnat.xsd</source>
<source>src/main/a/nonexistent/path</source>
</sources>
<!--
When providing xjcSourceExcludeFilters, the default exclude
Filter definitions are overridden by the Patterns supplied.
Any filter whose path ends with any of the Java Regular Expression Patterns
supplied will be excluded from the XJC sources. In this example,
files found under any of the source directories will be excluded from XJC
processing if their full paths end with '.xsd' or '.foo'
-->
<xjcSourceExcludeFilters>
<filter implementation="org.codehaus.mojo.jaxb2.shared.filters.pattern.PatternFileFilter">
<patterns>
<pattern>\.xsd</pattern>
<pattern>\.foo</pattern>
</patterns>
</filter>
</xjcSourceExcludeFilters>
<!--
Package name of the generated sources.
-->
<packageName>se.west</packageName>
<!--
Copy all source XSDs into the generate artifact.
Place them at the supplied xsdPathWithinArtifact, that is within the given directory.
-->
<xsdPathWithinArtifact>source/xsds</xsdPathWithinArtifact>
</configuration>
</plugin>
Unless xjcSourceExclude filters are given, standard excludes are in effect. These are:
- Files with the name “README.*”
- Files with the suffixes “.xml”, “.txt” or “.xjb”
- Files or Directories whose names starts with “.” (normally this implies hidden directories and setting files)
- Directories with the name “CVS”
Example 5: Multiple schemas with different configuration
In the case of having multiple XML schema files which should be processed with different configuration, you need to have multiple plugin execution bindings. One execution binding per unique configuration, as shown in the snippet below:
<plugin>
<groupId>org.codehaus.mojo</groupId>
<artifactId>jaxb2-maven-plugin</artifactId>
<version>${project.version}</version>
<executions>
<execution>
<id>xjc-schema1</id>
<goals>
<goal>xjc</goal>
</goals>
<configuration>
<!-- Use all XSDs under the west directory for sources here. -->
<sources>
<source>src/main/xsds/west</source>
</sources>
<!-- Package name of the generated sources. -->
<packageName>se.west</packageName>
</configuration>
</execution>
<execution>
<id>xjc-schema2</id>
<goals>
<goal>xjc</goal>
</goals>
<configuration>
<!-- Use all XSDs under the east directory for sources here. -->
<sources>
<source>src/main/xsds/east</source>
</sources>
<!-- Package name of the generated sources. -->
<packageName>se.east</packageName>
<!--
Don't clear the output directory before generating the sources.
Clearing the output directory removes the se.west schema from above.
-->
<clearOutputDir>false</clearOutputDir>
</configuration>
</execution>
</executions>
</plugin>
Example 6: Using an XML Java Binding file (“XJB”)
By default, the XjcMojo searches directory src/main/xjb (and the XjcTestMojo searches src/test/xjb) for external XML
schema generation binding files. Such files are used to control many aspects of the Java generation from XSD files;
please refer to the JAXB Reference Implementation for full details. However, a small XJB
file is found below.
<jxb:bindings version="1.0"
xmlns:jxb="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/jaxb"
xmlns:xsd="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema">
<!--
Change since version 2.0 of the j-m-p:
Note that the schemaLocation path must point to the XSD file
relative to *this* file, rather than the basedir.
-->
<jxb:bindings schemaLocation="../xsd/address.xsd" node="//xsd:schema">
<jxb:schemaBindings>
<jxb:package name="com.example.myschema"/>
</jxb:schemaBindings>
</jxb:bindings>
</jxb:bindings>
The JXB file above defines the package of the generated Java source code found in the XSD file ../xsd/address.xsd,
relative to the JXB file above. This implies that each JXB file must contain a path to the XSD files they tailor.
Each file found under within the JXB source directories is considered a JXB file, unless it is excluded by means of an
xjbExcludeFilter. A sample xjbExcludeFilter is found below; any file matching an xjbExcludeFilter is not used as a
binding file in the XJC compilation, implying that any file found within the standard XJB directory/directories are
not used if it ends with .txt or .xsd:
<configuration>
...
<xjbExcludeFilters>
<filter implementation="org.codehaus.mojo.jaxb2.shared.filters.pattern.PatternFileFilter">
<patterns>
<pattern>\.txt</pattern>
<pattern>\.xsd</pattern>
</patterns>
</filter>
</xjbExcludeFilters>
...
</configuration>
Just like the XJC source files, you can change the directories where the XjcMojo searches for binding files by
using the xjbSources configuration parameter. Each xjbSource element can be a relative path to a directory (in
which case all its files are searched and included recursively) or explicit files:
<configuration>
...
<xjbSources>
<xjbSource>src/dataexchange/special/aBindingConfiguration.xjb</xjbSource>
<xjbSource>src/dataexchange/xjbs</xjbSource>
</xjbSources>
...
</configuration>
Unless xjbExcludes filters are given, standard excludes are in effect. These are:
- Files with the name “README.*”
- Files with the suffixes “.xml”, “.txt” or “.xsd”
- Files or Directories whose names starts with “.” (normally this implies hidden directories and setting files)
- Directories with the name “CVS”
Example 7: Debugging jaxb2-maven-plugin executions
If you are curious about the exact java regexp patterns used for matching your files, or simply want to see what the
jaxb2-maven-plugin does internally, run the plugin in debug mode by adding the -X switch. The debug log contains
somewhat human-friendly log entries which contains the XJC arguments synthesized by the jaxb2-maven-plugin and
supplied in order:
+=================== [11 XJC Arguments]
|
| [0]: -xmlschema
| [1]: -encoding
| [2]: UTF-8
| [3]: -p
| [4]: com.example.myschema
| [5]: -d
| [6]: /Users/lj/Development/Projects/Codehaus/github_jaxb2_plugin/target/it/xjc-main/target/generated-sources/jaxb
| [7]: -extension
| [8]: -episode
| [9]: /Users/lj/Development/Projects/Codehaus/github_jaxb2_plugin/target/it/xjc-main/target/generated-sources/jaxb/META-INF/sun-jaxb.episode
| [10]: src/main/xsd/address.xsd
|
+=================== [End 11 XJC Arguments]
If you would like to run XJC manually in the same way as the jaxb2-maven-plugin runs the tool, simply paste the arguments given in the debug listing into a shell (separate with spaces).
The debug log also shows the configuration and result of the configured PatternFileFilters; as shown in the listing
below, two PatternFileFilters containing 3 java regular expression patterns each are applied to the files found below
the standard directory src/main/xsd. The listing shows the java regexps in use, and the resulting file after
removing all files identified by the two PatternFileFilters:
+=================== [Filtered sources]
|
| 2 Exclude patterns:
| [1/2]: Filter [PatternFileFilter]
| Processes nulls: [false]
| Accept on match: [true]
| 3 regularExpressions ...
| [0/3]: (\p{javaLetterOrDigit}|\p{Punct})+README.*
| [1/3]: (\p{javaLetterOrDigit}|\p{Punct})+\.xml
| [2/3]: (\p{javaLetterOrDigit}|\p{Punct})+\.txt
| [2/2]: Filter [PatternFileFilter]
| Processes nulls: [false]
| Accept on match: [true]
| 1 regularExpressions ...
| [0/1]: (\p{javaLetterOrDigit}|\p{Punct})+\.xjb
|
| 1 Standard Directories:
| [1/1]: src/main/xsd
|
| 1 Results:
| [1/1]: file:/Users/lj/Development/Projects/Codehaus/github_jaxb2_plugin/target/it/xjc-main/src/main/xsd/address.xsd
|
+=================== [End Filtered sources]
Also, the jaxb2-maven-plugin debug log contains debug log statements emitted from the underlying tools themselves
(SchemaGen or XJC). These statements may be formatted in somewhat strange ways, but starts with the name of the tool
encased in brackets. As illustrated below, the XJC tool emitted debug statements, one of which is from the
allowExternalAccess method indicating that the property http://javax.xml.XMLConstants/property/accessExternalSchema
is supported and successfully set:
[DEBUG] Using explicitly configured encoding [UTF-8]
[DEBUG] [XJC]: feb 03, 2015 3:39:32 EM com.sun.xml.bind.v2.util.XmlFactory createSchemaFactory
FINE: SchemaFactory instance: com.sun.org.apache.xerces.internal.jaxp.validation.XMLSchemaFactory@5b6813df
[DEBUG] [XJC]: feb 03, 2015 3:39:32 EM com.sun.xml.bind.v2.util.XmlFactory allowExternalAccess
FINE: Property "http://javax.xml.XMLConstants/property/accessExternalSchema" is supported and has been
successfully set by used JAXP implementation.
Yes … you get the timestamp for free …
Example 8: Setting the locale for the XJC execution
If you require the XJC tool to be executed with a default Locale other than your standard default Locale, simply use
the locale configuration parameter and supply a string parseable to a Locale on the form
<language>[,<country>[,<variant>]]. For example, to generate the XJC using french locale despite running Maven with
another Locale, configure the jaxb2-maven-plugin as follows:
<plugin>
<groupId>org.codehaus.mojo</groupId>
<artifactId>jaxb2-maven-plugin</artifactId>
<executions>
<execution>
<id>xjc</id>
<goals>
<goal>xjc</goal>
</goals>
</execution>
</executions>
<configuration>
<packageName>com.example.myschema</packageName>
<addGeneratedAnnotation>true</addGeneratedAnnotation>
<locale>fr</locale>
</configuration>
</plugin>
The generated source code will contain french comments:
/**
* <p>Classe Java pour AddressType complex type.
*
* <p>Le fragment de schéma suivant indique le contenu attendu figurant dans cette classe.
*
* <pre>
* <complexType name="AddressType">
* <complexContent>
* <restriction base="{http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema}anyType">
* <sequence>
* <element name="Name" type="{http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema}string"/>
* <element name="Line1" type="{http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema}string"/>
* <element name="Line2" type="{http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema}string"/>
* <element name="City" type="{http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema}string"/>
* <element name="State" type="{http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema}string"/>
* <element name="ZipCode" type="{http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema}decimal"/>
* </sequence>
* </restriction>
* </complexContent>
* </complexType>
* </pre>
*
*
*/
@XmlAccessorType(XmlAccessType.FIELD)
@XmlType(name = "AddressType", propOrder = {
"name",
"line1",
"line2",
"city",
"state",
"zipCode"
})
@Generated(value = "com.sun.tools.xjc.Driver", date = "2015-07-12T08:33:24+02:00", comments = "JAXB RI v2.2.11")
public class AddressType { .... }



